

May be used to reveal associated ligamentous injuries, osteochondral fractures and chondral fractures 7. fragment number and orientation/relationshipįor the same reasons, CT aids in treatment planning as well 6.
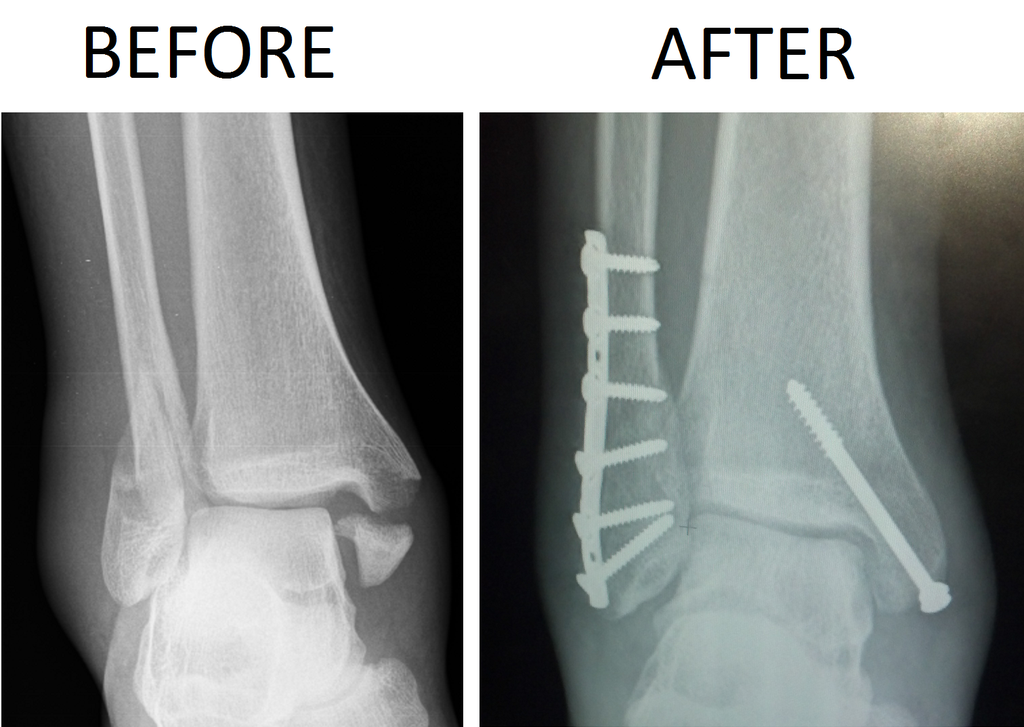
#Trimalleolar fx series
Standard ankle series suggested AP, lateral and mortise (best view to define displacement). The uncommon medial variation usually occurs with an adduction force 9. Pathology MechanismĮxternal rotation and supination is the main mechanism of injury in lateral triplane fractures. Possible signs include swelling, localized/referred pain, and/or deformity of the ankle. Symptoms comprise of pain and inability to weight bear. If intra-articular, called reverse Barton fracture BACK to TOPįracture dislocation involving the midtarsal joints in which there is superior dislocation of the navicular and cuboid bones on the talus and calcaneus BACK to TOPįracture of shaft of radius associated with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint-īaseball finger (a.k.a.In adolescents with closing epiphyseal plate(s) they are the most common ankle joint fractures - along with Tillaux fractures. Transverse fracture of distal radial metaphysis with palmar displacement of distal fracture fragment. May be associated with horizontal fracture through vertebral body BACK to TOP Horizontal fracture through spinous process with little or no compression of vertebral body. Transverse fracture of distal radial metaphysis proximal to joint with dorsal displacement and angulation of distal fragment BACK to TOP Most commonly through pubic rami and sacrum BACK to TOPĬonsists of isolated fracture of one iliac wing BACK to TOP Vertical shearing involves anterior & posterior arches. Hill-Sach’s (Fracture) Deformity -Results from anterior dislocation of humeral head- Located on posterolateral aspect of head BACK to TOPīennett’s Fracture- Intra-articular fracture of base of 1st metacarpal-įracture must involve 1st carpometacarpal joint BACK to TOPĪnterior tibiofibular ligament avulses small portion of tibia-Ĭonsists of avulsion of anterior lateral margin of distal tibia BACK to TOPĪ trimalleolar fracture of ankle with fractures of both malleoli and posterior lip of tibia BACK to TOPĪvulsion fracture of lateral tibial plateau at site of attachment of lateral capsular ligament-įrequently associated with tears of anterior cruciate ligament (70 %) or MCL or menisci BACK to TOPįractures through the pedicles of C2 with anterolisthesis of C2 on C3 BACK to TOP Lateral dislocation of talus and displacement of foot upward and outward-Rupture of distal talofibular ligaments BACK to TOP Jones Fracture- “True Jones" fracture occurs 1” distal to base of 5th metatarsal BACK to TOPĭupuytren’s Fracture- Fracture of distal fibula (lateral malleolus). Hoffa Fracture- Posterior tangential fracture of one (usually lateral) or both femoral condyles BACK to TOP Toddler’s Fracture- Subtle, non-displaced oblique fracture distal tibia in children - 9 months to 3 years of age BACK to TOP Wagon Wheel Fracture - Separation of distal femoral epiphysis from metaphysis of femur in a child BACK to TOPįracture of one or more spinous processes, most commonly C7 BACK to TOP Aviator’s Fracture-Fracture of neck of talusĬhauffer Fracture-AKA: Hutchinson's Fracture- Oblique fracture of radial styloid BACK to TOP


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
